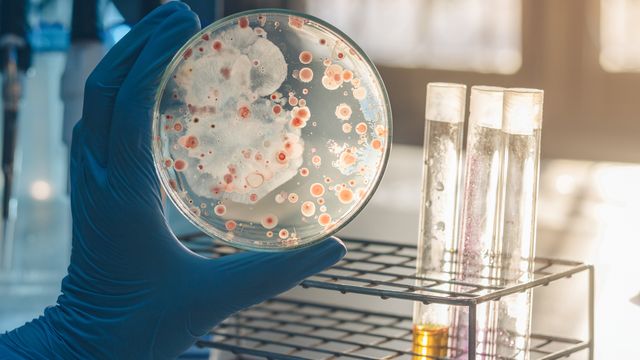
Microbial Culture Testing in Probiotic Products
In today’s competitive healthcare and wellness industries, the quality of probiotic products is paramount. This article explores microbial culture testing—a critical step in ensuring that these beneficial microorganisms are safe, effective, and consistently produced as intended.
The process involves isolating, identifying, and quantifying various strains within a probiotic supplement or food product. This ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as those set by the FDA for dietary supplements and foods.
The significance of microbial culture testing cannot be overstated, especially in the context of probiotics. These live microorganisms are expected to confer health benefits when consumed but must do so without causing harm or introducing contaminants. The testing process is designed to detect any deviations from the intended strains, which could lead to potential health risks.
Microbial culture testing typically involves several steps:
- Sample Collection: Collecting a representative sample of the probiotic product.
- Preparation: Preparing the sample for analysis, which may include dilution or plating techniques.
- Culture: Culturing the samples under controlled conditions to encourage growth and differentiation of microorganisms.
- Identification: Identifying specific strains using biochemical tests, genetic methods like PCR, or mass spectrometry.
- Quantification: Measuring the viable counts of different probiotic species present in the product.
The results from microbial culture testing are crucial for several reasons:
- To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and labeling accuracy.
- To maintain batch consistency, which is essential for quality control.
- To identify potential contaminants that could be harmful to consumers.
- To support the development of new probiotic products by validating strain efficacy and safety profiles.
Given the complexity of this testing, it is vital for laboratories to have state-of-the-art facilities equipped with advanced microbiological techniques. This ensures accurate results that can be trusted by both manufacturers and regulatory bodies alike.
Applied Standards
The microbial culture testing of probiotic products is governed by several international standards aimed at ensuring product safety, efficacy, and consistency. These include:
- ISO 14971:2019 Medical Devices - Application of Risk Management to Medical Devices: This standard provides guidelines for the application of risk management principles in the design and manufacturing processes of medical devices.
- ASTM E2386-15: Standard Practice for Establishing and Validating a Microbial Challenge Test: This practice sets out procedures to establish and validate microbial challenge tests used in the development, optimization, and qualification of packaging systems intended to protect against microorganisms.
- EN 1276:2008 Hygiene Requirements for Cleaning Agents Used in Food Premises - Microbiological Requirements: While not directly related to probiotics, this standard ensures that cleaning agents used in food premises meet strict hygiene standards which indirectly impact the quality of probiotic products.
These standards are essential frameworks that guide laboratories conducting microbial culture testing. Adherence to these guidelines helps ensure that test results are reliable and can be standardized across different laboratories and jurisdictions.
International Acceptance and Recognition
The microbial culture testing of probiotic products is widely recognized and accepted internationally due to its critical role in ensuring the safety, quality, and efficacy of these products. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), Health Canada, and others require compliance with these tests.
International acceptance extends beyond mere compliance; it also involves mutual recognition agreements that facilitate trade between countries. Laboratories recognized for their proficiency in microbial culture testing can perform analyses that are accepted globally without additional certification or retesting.
The importance of this international recognition cannot be overstated, as it allows for harmonization of standards and consistent quality assurance practices across borders. This not only simplifies regulatory compliance but also fosters innovation by encouraging cross-border collaboration in research and development.
Moreover, laboratories that meet these high standards are often preferred partners for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers who rely on accurate and reliable test results to ensure the safety of their products.
Environmental and Sustainability Contributions
The process of microbial culture testing in probiotic products contributes positively to environmental sustainability by ensuring that only safe, effective, and high-quality probiotics reach consumers. Here are some ways this testing supports sustainability:
- Elimination of Contaminants: By detecting harmful or unwanted microorganisms early in the production process, resources are conserved since contaminated products can be isolated before they enter the market.
- Reduction in Waste: Accurate testing reduces the likelihood of batch failures due to contamination or substandard product quality. This minimizes waste and resource consumption associated with rework or recall.
- Innovation in Packaging: By validating packaging efficacy through microbial challenge tests, less wasteful and more sustainable packaging solutions can be developed.
- Economic Efficiency: Accurate testing helps manufacturers avoid costly recalls and reputational damage. This leads to better resource allocation and overall economic efficiency.
The commitment to sustainability through microbial culture testing is a key factor in maintaining the integrity of probiotic products, ensuring they meet stringent quality standards while minimizing environmental impact.