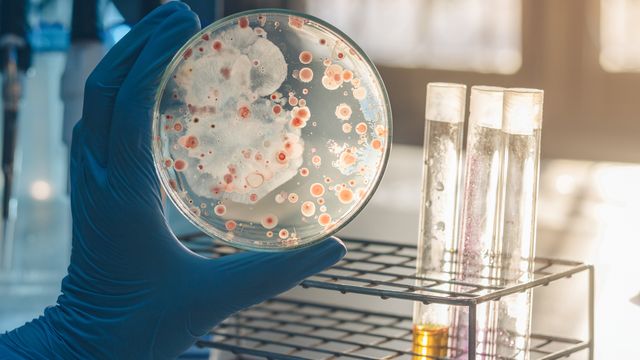
Enterococcus spp. Culture Testing in Food Hygiene Studies
The detection and identification of Enterococcus species, particularly in food hygiene studies, are crucial for maintaining food safety standards. This bacterium is a significant indicator organism used to assess the hygienic conditions during food production and processing. It belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and includes several species such as E. faecalis and E. faecium, which have the potential to cause infections in humans, especially those with weakened immune systems.
The significance of Enterococcus spp. testing lies in its ability to survive harsh environmental conditions, such as high levels of antimicrobial agents. This makes it a useful indicator for monitoring sanitation practices and ensuring that food processing environments meet stringent hygiene standards. Inadequate control measures can lead to contamination, which may result in health risks including urinary tract infections, bacteremia, endocarditis, and meningitis.
In the context of food hygiene studies, the presence of Enterococcus spp. serves as a proxy for fecal contamination. This is because these bacteria are predominantly found in the gastrointestinal tracts of warm-blooded animals, including humans. Therefore, their detection can indicate poor sanitation practices or inadequate cleaning processes within food production facilities.
The testing methodology typically involves the use of selective media that favor the growth of Enterococcus spp., such as MRS (Mast-Revill-Schweiger) agar. This process allows for accurate differentiation between different species, which is vital for understanding the microbial ecology and potential sources of contamination within a facility.
The results from these tests are critical for identifying areas where improvements in hygiene practices are necessary. By implementing more stringent cleaning protocols and monitoring programs, facilities can reduce the likelihood of cross-contamination and ensure compliance with international standards such as ISO 22000:2018.
Given the importance of this testing in maintaining food safety, it is essential to choose a laboratory that offers reliable and accurate results. Our state-of-the-art facility utilizes advanced microbiological techniques and equipment to ensure precision and consistency in our tests. We employ experienced professionals who are well-versed in current best practices, ensuring that clients receive actionable insights into their hygiene management systems.
Why It Matters
The presence of Enterococcus spp. in food products or processing environments can have serious implications for public health and the reputation of food producers. Poor hygiene practices, such as inadequate cleaning or handling of contaminated raw materials, can lead to the introduction of these bacteria into foodstuffs.
- Health Risks: Enterococcus spp., especially species like E. faecalis, are opportunistic pathogens that can cause severe infections in immunocompromised individuals. This underscores the critical need for stringent hygiene measures in food processing.
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO), have strict guidelines regarding microbial contamination levels in foods. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in product recalls and legal penalties.
- Customer Trust: Consumers increasingly demand transparency and assurance about the safety of their food products. The presence of Enterococcus spp. can erode this trust, leading to a loss of market share for affected brands.
- Economic Impact: Recalls due to contamination by Enterococcus spp. can be extremely costly, affecting both production schedules and revenue streams. Implementing robust hygiene measures early on can mitigate these risks effectively.
In summary, the importance of Enterococcus spp. culture testing in food hygiene studies cannot be overstated. It serves as a vital tool for maintaining public health, ensuring regulatory compliance, protecting brand reputation, and safeguarding economic stability within the food industry.
Scope and Methodology
The scope of our Enterococcus spp. culture testing service encompasses various aspects of food hygiene studies aimed at identifying potential sources of contamination. Our methodology follows international standards such as ISO 16954:2013, which provides guidelines for the isolation and identification of Enterococcus species in foods.
The process begins with sample collection from different stages of food production, including raw materials, processing equipment, and final products. Samples are then prepared according to standardized procedures before being inoculated onto selective media designed specifically for Enterococcus spp. growth.
Culture conditions vary depending on the specific requirements of each study but generally involve incubation at 35°C ± 1°C for approximately 48 hours. During this period, any colonies suspected to be Enterococcus spp. are carefully observed and characterized using phenotypic characteristics such as colony morphology, biochemical reactions, and susceptibility testing.
To further confirm the identity of isolated strains, molecular methods like PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) may also be employed. This ensures that only true Enterococcus spp., rather than closely related species, are reported in our findings.
The final step involves compiling detailed reports summarizing all observations and conclusions drawn from the tests conducted. These reports provide valuable insights into current hygiene practices within a facility and highlight any areas requiring attention or improvement.
Use Cases and Application Examples
Enterococcus spp. culture testing finds application in multiple sectors including food manufacturing, hospitality, and healthcare facilities. Here are some illustrative examples:
- Food Manufacturing: A major bakery chain conducted regular Enterococcus spp. tests as part of its quality assurance program to ensure that all products were free from microbial contamination.
- Hospitality: A luxury hotel implemented strict hygiene protocols after detecting Enterococcus spp. in its kitchen, leading to improved cleanliness standards across all departments.
- Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals use this testing method during outbreaks of nosocomial infections to trace back possible sources and prevent further spread within the institution.
In each case, successful implementation of proper hygiene measures resulted in significant reductions in microbial contamination rates and enhanced overall safety standards. By adhering to these protocols, organizations can protect both staff members and consumers from potential health risks associated with contaminated food or environments.