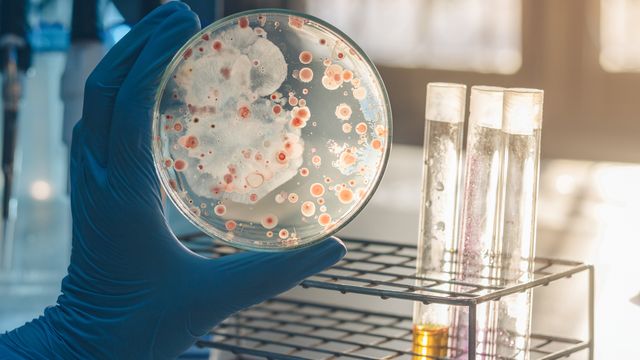
Candida spp. Culture Testing in Veterinary Pathology
In veterinary pathology, Candida species testing is a critical diagnostic tool used to identify and quantify Candida spp. that cause infections. These tests are especially important for monitoring the effectiveness of antifungal therapy and ensuring appropriate treatment protocols. The primary goal of this culture-based test is to provide accurate identification of Candida species in veterinary specimens, which can then inform clinical decisions.
The process begins with proper specimen collection, which typically involves swabs from infected areas or blood samples for systemic infections. Specimens are inoculated onto specialized media that supports the growth of Candida spp. Growth is monitored over several days to ensure accurate identification using colony morphology, color changes, and other visual characteristics.
The significance of this test in veterinary medicine cannot be overstated. It allows for a detailed understanding of the pathogen's presence and helps tailor treatments more effectively. For instance, some Candida species are more resistant to certain antifungal drugs, making it vital to identify the strain accurately before initiating treatment.
The use of advanced microbiological techniques ensures that this test remains at the forefront of diagnostic capabilities. Modern laboratories employ high-resolution microscopes and automated systems for faster results. These technologies not only enhance accuracy but also reduce turnaround times, enabling quicker intervention when necessary.
However, the reliability of these tests depends heavily on proper specimen handling and interpretation by trained personnel. This underscores the importance of continuing education and staying abreast of updates in diagnostic methods to maintain high standards of care.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Evaluation of Antifungal Therapy Efficacy | Determining whether the current treatment is effective by monitoring changes in Candida colonization. |
| Identification of Drug-Resistant Strains | Identifying resistant strains to guide appropriate antifungal therapy choices. |
| Detection of Systemic Infections | Monitoring for signs of Candida in blood or other systemic sites. |
| Prevention of Nosocomial Infections | Identifying sources of contamination in hospital settings to prevent spread. |
The benefits of this test are manifold. It provides early detection, aids in selecting appropriate treatments, and helps monitor the progression of infections. This is particularly crucial given the increasing prevalence of drug-resistant pathogens in veterinary medicine. By using accurate culture methods, veterinarians can make informed decisions that improve patient outcomes.
Why Choose This Test
The Candida spp. culture test stands out as a reliable diagnostic tool for several reasons:
- It offers precise identification of Candida species, which is essential for targeted treatment.
- The use of advanced media ensures consistent and accurate results.
- It supports the evaluation of antifungal therapy efficacy, leading to better patient outcomes.
- The test can detect drug-resistant strains early on, guiding appropriate therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, this culture-based approach complements other diagnostic methods, providing a comprehensive picture of the infection. The ability to monitor changes in colonization over time is particularly valuable for systemic infections and nosocomial outbreaks. This comprehensive approach ensures that veterinarians have all necessary information at their disposal when making critical decisions.
International Acceptance and Recognition
The Candida spp. culture test has gained widespread recognition in the veterinary community, with international standards providing a benchmark for quality assurance. Compliance with these guidelines ensures consistent results across different laboratories worldwide:
- ISO/IEC 17025: Laboratory accreditation to ensure technical competence and reliability.
- AAMI TIR43-2016: Recommended practices for microbiology laboratories, emphasizing best practices in specimen handling and testing.
- CLSI M26-A: Guidelines for the performance of antifungal susceptibility testing, which aligns with culture-based methods.
The acceptance of this test by major veterinary organizations further reinforces its importance. Organizations such as the American College of Veterinary Pathologists (ACVP) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) recommend these tests as part of routine diagnostic procedures. This global consensus underscores the value of Candida spp. culture testing in maintaining high standards of veterinary care.
Use Cases and Application Examples
The application of Candida spp. culture testing spans various scenarios within veterinary medicine:
- Evaluation of Antifungal Therapy Efficacy: Monitoring changes in Candida colonization over time to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
- Identification of Drug-Resistant Strains: Detecting resistance patterns early on to guide appropriate antifungal therapy choices.
- Detection of Systemic Infections: Identifying Candida in blood or other systemic sites, aiding in the management of severe infections.
- Prevention of Nosocomial Infections: Monitoring for signs of contamination and preventing spread within hospital settings.
The following table provides a more detailed look at these use cases:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Evaluation of Antifungal Therapy Efficacy | Determining whether the current treatment is effective by monitoring changes in Candida colonization. |
| Identification of Drug-Resistant Strains | Identifying resistant strains to guide appropriate antifungal therapy choices. |
| Detection of Systemic Infections | Monitoring for signs of Candida in blood or other systemic sites. |
| Prevention of Nosocomial Infections | Identifying sources of contamination in hospital settings to prevent spread. |
The real-world application of these tests is exemplified by their use in large veterinary hospitals and research institutions. For instance, the identification of drug-resistant strains helps prevent the spread of resistant organisms within the hospital, thereby protecting other patients from potentially life-threatening infections. This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also contributes to overall public health.