UL 583 Battery Powered Vehicle Safety Testing with ADAS
The Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standard UL 583 is a critical benchmark for ensuring the safety of battery-powered vehicles. This standard addresses various aspects of vehicle safety, including electrical systems, structural integrity, and thermal management. When combined with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), these tests become even more crucial as they ensure that all components work seamlessly to enhance both driver safety and operational reliability.
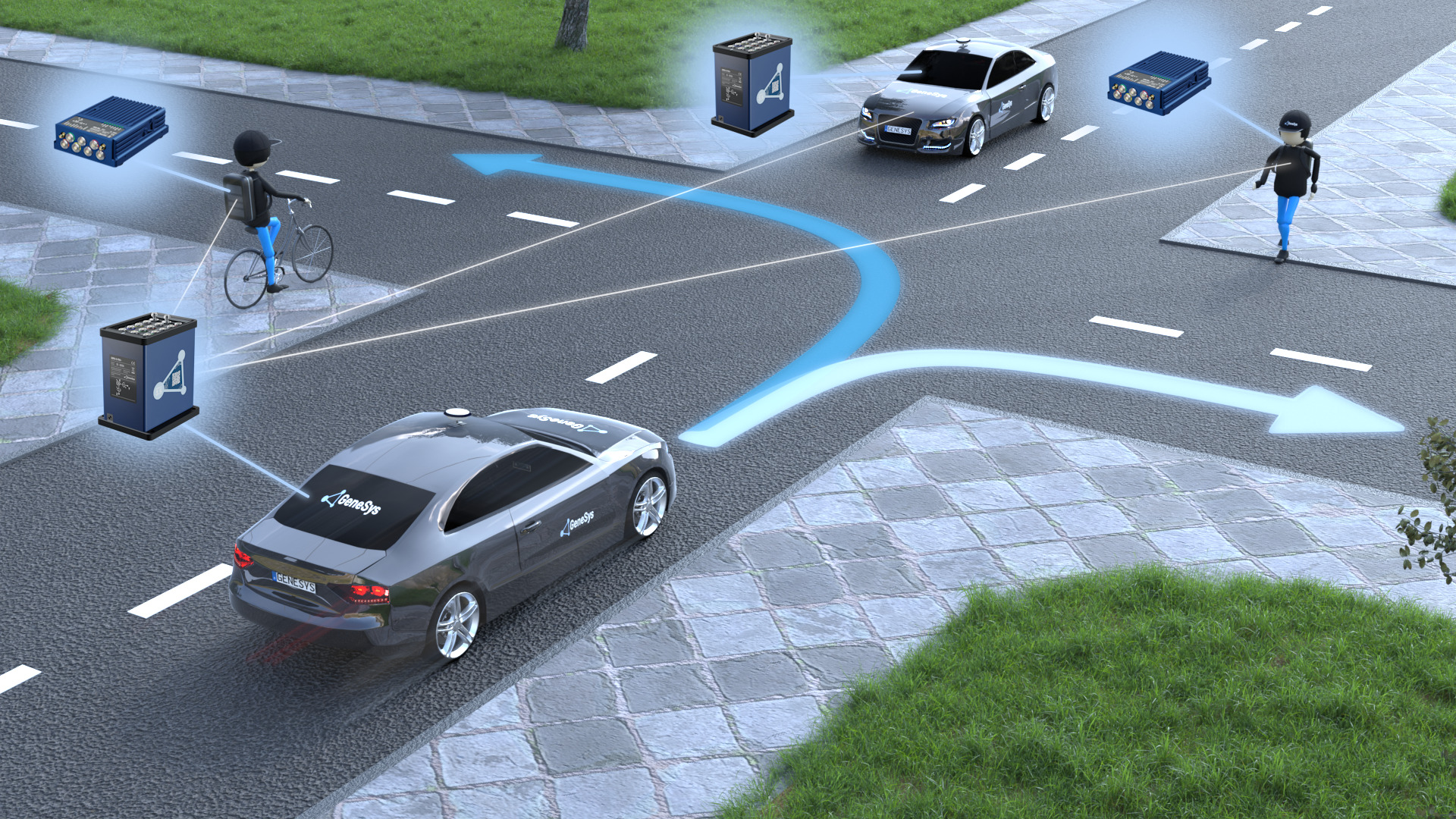
In the context of autonomous vehicles and ADAS, UL 583 testing goes beyond traditional safety checks. It ensures that battery-powered vehicles meet stringent requirements for electrical compatibility with other vehicle systems, including sensors, cameras, radar units, and LiDAR devices used in ADAS. This integration is vital because even a minor issue can compromise the overall performance of an autonomous system.
The testing process involves rigorous simulations designed to replicate real-world driving scenarios. For instance, engineers subject vehicles to extreme conditions such as cold starts, high-speed braking, sharp turns, and sudden accelerations. These tests are aimed at identifying potential weaknesses in the battery management systems (BMS) and ensuring that they can handle these stresses without overheating or causing malfunctions.
Another critical aspect of UL 583 testing is its focus on thermal management. In autonomous vehicles equipped with ADAS, the heat generated by various components must be carefully managed to prevent performance degradation or safety risks. The tests ensure that the vehicle's cooling systems are effective enough to maintain optimal operating temperatures under all driving conditions.
Moreover, UL 583 compliance involves thorough validation of electrical compatibility between different subsystems within the vehicle. This includes ensuring that battery-powered systems can safely interact with other critical components like braking systems, steering mechanisms, and communication networks used in ADAS. Any misalignment or interference could lead to catastrophic failures during autonomous driving.
The testing process also evaluates the durability and reliability of the entire electrical architecture. Engineers simulate long-term usage scenarios to assess how well each component holds up over extended periods. This longevity is particularly important for autonomous vehicles that may operate continuously without human intervention, requiring robust systems capable of enduring continuous stress.
Compliance with UL 583 also extends to ensuring that battery-powered vehicles meet stringent performance criteria when integrated into advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These tests verify the accuracy and reliability of ADAS features such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automated emergency braking. By adhering strictly to these standards, manufacturers can enhance public trust in autonomous technologies while minimizing risks associated with safety-critical failures.
It is essential for organizations involved in developing or procuring battery-powered vehicles intended for use within the autonomous vehicle market to understand the importance of UL 583 compliance. Meeting this standard not only enhances overall safety but also aligns with global regulatory requirements and industry best practices. By prioritizing adherence to these standards, companies can ensure that their products meet high-quality benchmarks set forth by leading organizations like Underwriters Laboratories.
For quality managers, compliance officers, R&D engineers, and procurement professionals working in this sector, understanding the intricacies of UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing with ADAS is crucial. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions about product development, supplier selection, regulatory compliance, and market positioning.
Why It Matters
The significance of adhering to the UL 583 standard cannot be overstated when it comes to ensuring the safety and reliability of battery-powered vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These tests play a pivotal role in safeguarding both passengers and pedestrians by minimizing the risk of accidents caused by electrical malfunctions or structural failures.
One key reason for this emphasis is the increasing adoption of autonomous driving technology. As more vehicles integrate sophisticated ADAS features, such as collision avoidance systems and adaptive cruise control, it becomes imperative to ensure that all components operate flawlessly under various conditions. Any failure in these integrated systems could have severe consequences, ranging from minor inconveniences to life-threatening incidents.
The tests conducted under UL 583 not only focus on the safety of individual subsystems but also evaluate their integration within a larger system. This holistic approach ensures that all parts work together harmoniously without causing interference or failures. By doing so, manufacturers can build confidence among consumers and regulatory bodies regarding the reliability and safety of autonomous vehicles.
Another crucial aspect is the emphasis on durability and longevity in battery-powered systems. Given the high cost associated with purchasing advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), it's essential that these components remain functional over extended periods without requiring frequent maintenance or replacement. UL 583 testing helps manufacturers achieve this goal by subjecting vehicles to extensive simulations designed to replicate real-world driving scenarios.
Moreover, compliance with the UL 583 standard ensures compatibility between different subsystems within a vehicle. In autonomous vehicles equipped with ADAS, various systems need to communicate seamlessly and function cohesively. Any discrepancy or misalignment could lead to performance degradation or even complete system failure. By conducting thorough testing, manufacturers can identify potential issues early on and address them before releasing products into the market.
From a regulatory perspective, adhering to UL 583 is becoming increasingly important as governments around the world introduce stricter safety standards for autonomous vehicles. Meeting these requirements not only helps companies avoid costly penalties but also enhances their reputation among consumers seeking safe and reliable transportation options. By prioritizing compliance with this standard, manufacturers can stay ahead of regulatory changes while maintaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
In summary, UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing with ADAS is essential for ensuring that all components work together seamlessly to enhance both driver safety and operational reliability. This rigorous process helps identify potential weaknesses early on, allowing manufacturers to address them before releasing products into the market. Ultimately, this commitment to quality contributes to greater public trust in autonomous technologies while minimizing risks associated with safety-critical failures.
Applied Standards
The UL 583 standard for battery-powered vehicle safety testing is based on several internationally recognized standards that form the backbone of automotive safety and reliability. These include ISO, ASTM, EN, IEC, SAE International, and other industry-specific guidelines.
One key international standard relevant to this service is ISO 26262, which provides a framework for functional safety in automotive engineering. This standard emphasizes risk assessment and management throughout the entire lifecycle of an autonomous vehicle, ensuring that all potential hazards are identified and mitigated effectively. By adhering to ISO 26262 guidelines during UL 583 testing, manufacturers can ensure that their battery-powered vehicles meet stringent requirements for electrical compatibility with other systems.
Another important standard is ASTM F42, which deals specifically with the design and development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). This standard outlines best practices for integrating ADAS features into vehicle designs, focusing on interoperability between different subsystems. By following ASTM F42 guidelines during UL 583 testing, manufacturers can ensure that their battery-powered vehicles are capable of safely interacting with various sensors and cameras used in ADAS.
EN 15027 is another relevant standard that addresses the safety aspects of electrical components within automotive systems. This European standard provides detailed requirements for the design, manufacturing, and testing of these components to ensure they meet stringent quality standards. By incorporating EN 15027 into UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing, manufacturers can verify that their vehicles comply with all necessary regulations regarding electrical compatibility.
IEC 61508 is an international standard for the design and production of electronic systems used in automotive applications. This standard focuses on functional safety by providing guidelines for minimizing risks associated with malfunctions or failures within these systems. By following IEC 61508 during UL 583 testing, manufacturers can ensure that their battery-powered vehicles meet rigorous standards for electrical compatibility.
SAE J2714 is a standard developed by SAE International that specifies requirements and procedures for the design, development, validation, verification, and certification of ADAS systems. This standard covers various aspects of ADAS functionality, including performance metrics, testing methodologies, and acceptance criteria. By adhering to SAE J2714 guidelines during UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing, manufacturers can ensure that their vehicles meet all necessary requirements for safe operation.
These internationally recognized standards work together to provide comprehensive coverage of the various aspects involved in ensuring the safety and reliability of battery-powered vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). By following these guidelines during UL 583 testing, manufacturers can verify that their products meet all necessary regulatory requirements while maintaining high-quality benchmarks.
Scope and Methodology
The scope of UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing with ADAS is extensive, covering a wide range of tests designed to ensure the integrity, reliability, and overall safety of these vehicles. The methodology involves several key steps that are critical for achieving compliance.
Firstly, engineers begin by preparing the test specimens according to specified procedures outlined in UL 583. This includes assembling the battery-powered vehicle with all necessary components, including ADAS features like cameras, radar units, and LiDAR devices. Once assembled, the vehicle undergoes initial inspections to ensure that it meets basic quality control standards.
The next step involves subjecting the vehicle to various stress tests aimed at identifying potential weaknesses or areas of concern. These tests simulate real-world driving scenarios such as cold starts, high-speed braking, sharp turns, and sudden accelerations. By replicating these conditions in a controlled environment, engineers can pinpoint any issues that may arise under extreme circumstances.
A critical component of UL 583 testing is evaluating the thermal management systems within battery-powered vehicles. In autonomous driving scenarios, heat generated by various components must be carefully managed to prevent performance degradation or safety risks. The tests ensure that the cooling systems are effective enough to maintain optimal operating temperatures under all driving conditions.
Compliance with UL 583 also involves rigorous validation of electrical compatibility between different subsystems within the vehicle. This includes ensuring that battery-powered systems can safely interact with other critical components like braking systems, steering mechanisms, and communication networks used in ADAS. Any misalignment or interference could lead to catastrophic failures during autonomous driving.
Another important aspect is the durability and reliability of the entire electrical architecture. Engineers simulate long-term usage scenarios to assess how well each component holds up over extended periods. This longevity is particularly important for autonomous vehicles that may operate continuously without human intervention, requiring robust systems capable of enduring continuous stress.
In addition to these tests, UL 583 battery-powered vehicle safety testing with ADAS also evaluates the performance and accuracy of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). These features include collision avoidance systems, lane-keeping assist, and automated emergency braking. By adhering strictly to this standard, manufacturers can enhance public trust in autonomous technologies while minimizing risks associated with safety-critical failures.
The testing process is meticulously documented throughout every stage, ensuring transparency and traceability. Detailed reports are generated detailing the results of each test conducted. These reports serve as important references for quality managers, compliance officers, R&D engineers, and procurement professionals involved in developing or procuring battery-powered vehicles intended for use within the autonomous vehicle market.