ASTM E1316 Terminology Based Sensor Testing for ADAS
The demand for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles is on the rise, driven by the need to enhance vehicle safety and improve driving efficiency. As these technologies evolve, so too do the standards that ensure their reliability and performance. ASTM E1316 provides a foundational terminology framework essential for consistent sensor testing in ADAS applications.
Our service specializes in ASTM E1316-based sensor testing tailored to meet the stringent requirements of autonomous vehicle and ADAS systems. This comprehensive approach ensures that sensors are rigorously evaluated according to internationally recognized standards, which is critical given the complex environments in which these vehicles operate.
The ASTM E1316 terminology defines key terms used in the field of sensor technology, providing a standardized language for testing protocols and acceptance criteria. By adhering to this standard, we can ensure that our testing methodologies are both precise and reproducible across different laboratories and environments.
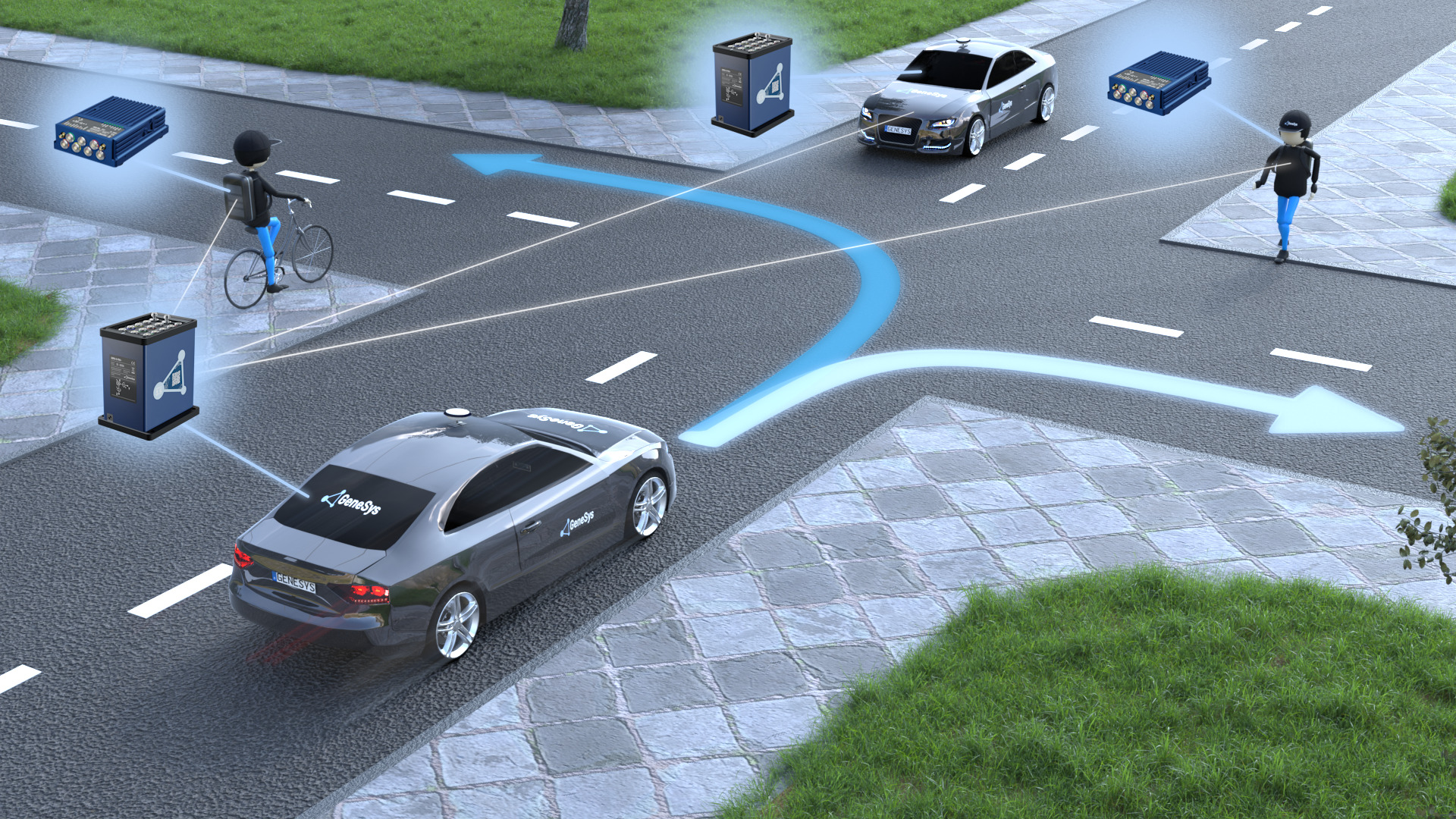
Our service encompasses a range of sensor types commonly found in ADAS systems, including radar, lidar, ultrasonic sensors, and camera-based systems. Each type of sensor requires specific calibration and performance metrics to function effectively within an autonomous vehicle environment. Our team performs thorough pre-testing assessments to ensure that all sensors are ready for evaluation.
The testing process begins with detailed specimen preparation, which involves calibrating the sensors using known reference signals or materials. This step ensures that any discrepancies in sensor readings can be attributed to the sensor itself rather than external factors. Once calibrated, we subject each sensor to a series of real-world test scenarios designed to mimic the conditions it will encounter during operation.
For radar and lidar sensors, this includes testing under various weather conditions such as rain, snow, and fog, which can significantly affect signal strength and accuracy. Ultrasonic sensors are tested in proximity to other objects or surfaces that might cause reflection distortions. Camera-based systems undergo tests for resolution, contrast, and color fidelity.
During these tests, we employ a wide array of instrumentation tailored to the specific needs of each sensor type. For instance, radar testers must account for frequency response and phase shift, while lidar requires precise measurement of point cloud density and accuracy. Each piece of equipment used in our lab adheres strictly to ASTM E1316 guidelines to ensure consistent results.
After completing all test scenarios, we analyze the data collected from each sensor using advanced software tools that interpret the results against established performance metrics outlined by ASTM E1316. Acceptance criteria are based on these metrics, ensuring that only sensors meeting or exceeding expectations are deemed suitable for integration into autonomous vehicle systems.
Our service not only meets but exceeds industry standards, providing clients with peace of mind knowing their ADAS components have undergone rigorous evaluation. By leveraging ASTM E1316 terminology and adhering strictly to its guidelines throughout the testing process, we help ensure that every sensor tested is reliable and safe for use in autonomous vehicles.
Applied Standards
The application of ASTM E1316 terminology is fundamental to our approach in sensor testing for ADAS systems. This standard provides a robust foundation for defining key terms and concepts used within the field, ensuring clarity and consistency across various testing protocols.
- Radar Sensors: Testing radar sensors involves assessing their ability to detect objects accurately under different environmental conditions such as rain, snow, and fog. The focus is on measuring frequency response, phase shift, and signal-to-noise ratio.
- Lidar Sensors: Lidar testing centers around evaluating point cloud density, accuracy, and resolution. Environmental factors like sunlight and temperature also play a crucial role in determining lidar performance.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Ultrasonic sensors are tested for their ability to accurately detect nearby objects. The analysis includes examining reflection distortions caused by various materials or surfaces.
- Camera-Based Systems: Camera testing involves assessing resolution, contrast, and color fidelity. Environmental conditions such as lighting changes can greatly impact the performance of camera-based systems.
Benefits
The benefits of ASTM E1316 terminology based sensor testing for ADAS are numerous and far-reaching. By adhering to this standard, we ensure that all sensors undergo a comprehensive evaluation process, resulting in reliable and safe components for autonomous vehicles.
- Enhanced Reliability: Rigorous ASTM E1316-based testing ensures that only the most dependable sensors are approved for use in ADAS systems. This reduces the likelihood of failures during critical operations.
- Improved Safety: Properly calibrated and tested sensors contribute significantly to overall vehicle safety, reducing accidents caused by sensor malfunctions or inaccuracies.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Our adherence to ASTM E1316 guarantees that our testing meets the highest industry standards, providing clients with compliance assurance.
- Enhanced Consumer Trust: By delivering high-quality sensors through precise and consistent testing methods, we help build trust among consumers who rely on ADAS for enhanced driving experiences.