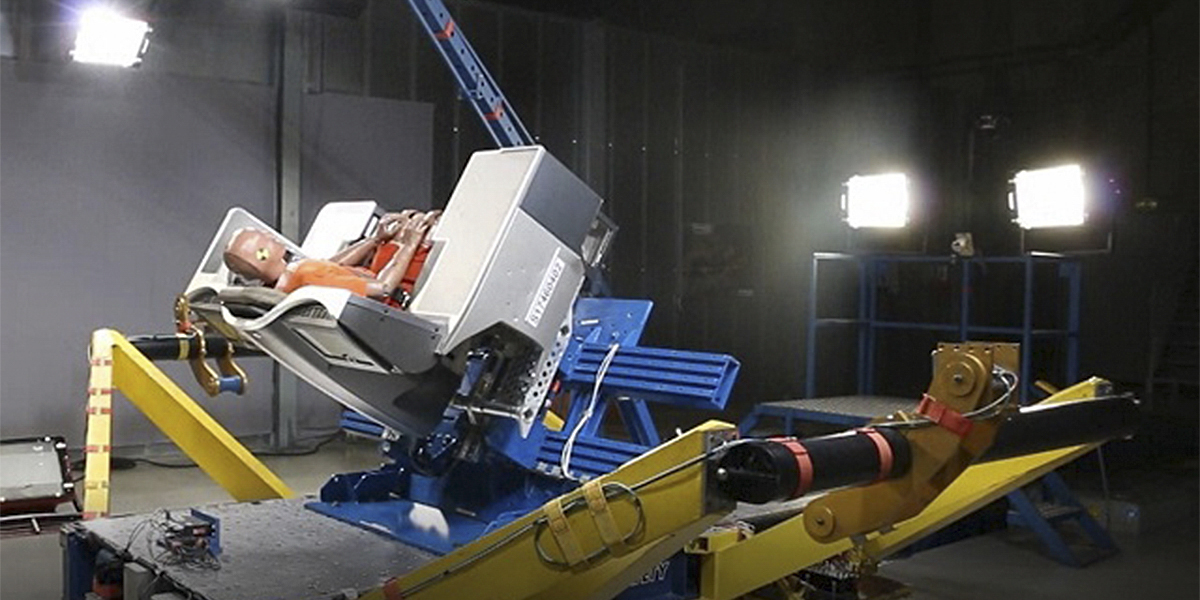
Passive Safety Systems Testing
The automotive industry places a premium on safety. Passive safety systems are an integral part of this commitment, designed to protect occupants in the event of a collision. This service page focuses on the testing methodologies and standards used to ensure these systems meet rigorous performance criteria.
Passive safety is defined as the measures that mitigate injury during or after a crash. It encompasses seat belts, airbags, structural integrity, and other components designed to protect passengers in the event of a collision. Testing passive safety systems involves evaluating their effectiveness under simulated crash conditions using controlled environments such as crash test dummies and high-impact testing machines.
The testing process begins with specimen preparation. This includes ensuring that all components are installed correctly according to manufacturer specifications, and that the vehicle is in optimal condition for testing. The methodology typically adheres to international standards like ISO 6482:2015, which specifies test procedures for seat belts, as well as other relevant standards such as UN ECE R94.
The scope of testing can be extensive and includes multiple crash scenarios designed to replicate real-world conditions. This ensures that the passive safety systems perform reliably under a variety of circumstances. Testing is conducted in controlled environments to ensure consistent results and repeatability. The use of sophisticated instrumentation such as high-speed cameras, accelerometers, and force sensors allows for precise measurement of forces and displacements during impact.
Once testing is complete, the data collected is analyzed using advanced software tools. This analysis provides insights into how well each system performed under various crash conditions. Reporting is comprehensive and detailed, outlining the performance metrics of each component tested. This includes measures such as deployment times for airbags, force distribution across seat belts, and structural integrity of the vehicle frame.
Compliance with international standards ensures that vehicles meet safety requirements set by regulatory bodies worldwide. For instance, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) requires manufacturers to meet certain passive safety standards through rigorous testing protocols. Compliance is crucial for ensuring consumer safety and maintaining market access in various regions.
The automotive industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on advanced materials and innovative designs that enhance passive safety. Testing plays a critical role in this evolution by providing actionable data that informs design improvements and regulatory compliance.
Scope and Methodology
The scope of passive safety systems testing is comprehensive, covering all components designed to protect occupants during a crash. This includes airbags, seat belts, structural integrity, energy management systems, and other features aimed at mitigating injury.
The methodology involves simulating various crash scenarios using controlled environments such as crash test dummies and high-impact testing machines. The tests are conducted in compliance with international standards like ISO 6482:2015 for seat belts and UN ECE R94 for side impact protection systems. The process begins with specimen preparation, ensuring that all components are installed correctly according to manufacturer specifications.
The methodology includes several key steps:
- Preparation: Specimens are prepared by installing passive safety components in vehicles and ensuring they meet the required specifications.
- Simulation: Controlled environments simulate various crash scenarios using sophisticated instrumentation such as high-speed cameras, accelerometers, and force sensors to measure performance metrics.
- Analysis: Data collected during testing is analyzed using advanced software tools to provide insights into component performance. This includes measures such as deployment times for airbags, force distribution across seat belts, and structural integrity of the vehicle frame.
- Reporting: Comprehensive reports are generated that outline the performance metrics of each component tested. Compliance with international standards is ensured through rigorous testing protocols set by regulatory bodies worldwide.
The use of advanced instrumentation allows for precise measurement of forces and displacements during impact, providing valuable data for further improvements in passive safety systems.
Benefits
Testing passive safety systems is essential for ensuring the highest level of protection for vehicle occupants. By adhering to rigorous testing protocols, manufacturers can ensure that their vehicles meet or exceed international standards and regulatory requirements. This not only enhances consumer confidence but also contributes to a safer driving experience.
The benefits of thorough testing are numerous:
- Enhanced Safety: Testing ensures that passive safety systems perform effectively under various crash conditions, providing reliable protection for passengers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting international standards and regulatory requirements is crucial for maintaining market access in different regions.
- Improved Design: Data collected during testing provides valuable insights into component performance, informing design improvements and innovations.
- Consumer Trust: Ensuring high levels of safety through rigorous testing builds trust with consumers, enhancing brand reputation.
- Reduced Liability Risks: Compliance with international standards reduces the risk of legal action related to vehicle safety issues.
- Innovative Development: Testing helps identify areas for improvement and innovation in passive safety systems.
- Cost Savings: Early detection of design flaws through testing can save significant costs by avoiding costly recalls later on.
- Maintaining Reputation: Ensuring high standards in product safety helps maintain a positive brand image and customer loyalty.
The automotive industry's commitment to safety is reflected in the rigorous testing protocols used for passive safety systems. This ensures that vehicles meet or exceed international standards, enhancing consumer confidence and contributing to a safer driving experience.
Industry Applications
| Component | Test Scenario | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Airbags | Frontal Impact | Deployment Time, Force Distribution |
| Seat Belts | Side Impact | Retractor Functionality, Buckling Speed |
| Structural Integrity | Roll Over Test | Bending Strength, Crumple Zone Performance |
| Energy Management Systems | Crash Energy Distribution | Energy Absorption Rates |
The testing of passive safety systems has numerous applications across the automotive industry. For instance, airbags are tested in frontal impact scenarios to ensure they deploy correctly and provide optimal protection for occupants. Seat belts undergo side impact tests to evaluate their retractor functionality and buckling speed. Structural integrity is assessed through roll over tests to determine bending strength and crumple zone performance. Energy management systems are evaluated based on crash energy distribution, focusing on absorption rates.
These tests ensure that each component of the passive safety system performs effectively under various crash conditions, providing reliable protection for passengers. By adhering to rigorous testing protocols, manufacturers can meet or exceed international standards and regulatory requirements, enhancing consumer confidence and contributing to a safer driving experience.