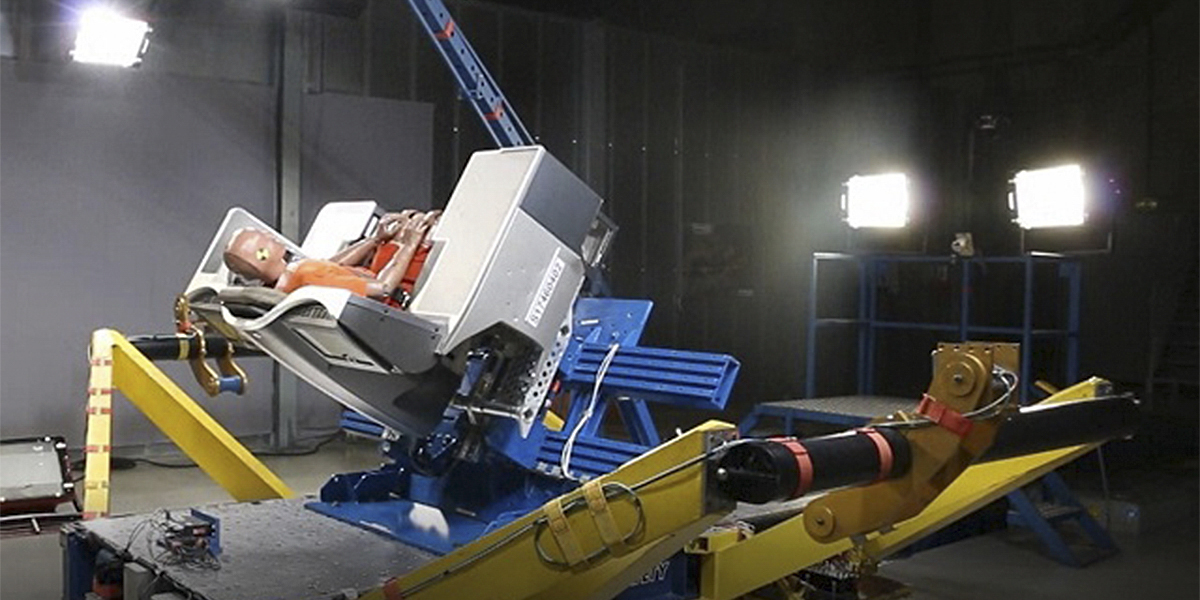
GB T31485 Fuel Cell Vehicle Passive Safety Airbag Test
The GB/T 31485 standard is a crucial document in the realm of automotive safety testing, particularly for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). It focuses on assessing the passive safety systems within these vehicles, ensuring they meet stringent performance criteria to protect occupants during accidents. This test evaluates how well the airbag system functions when deployed under simulated crash conditions.
GB/T 31485 specifies a series of tests that simulate real-world crash scenarios to determine the effectiveness of the passive safety systems in fuel cell vehicles. These tests are designed to mimic various types of collisions, including frontal impacts and side impacts at different speeds and angles. By doing so, they help manufacturers identify potential weaknesses in their designs and improve overall vehicle safety.
The test involves deploying airbags under controlled conditions that replicate the forces experienced during a crash. The goal is to ensure the airbag system operates correctly, providing adequate protection for occupants without causing harm through over-inflation or improper deployment timing. Compliance with this standard ensures that fuel cell vehicles meet minimum safety requirements set by regulatory bodies.
For quality managers and compliance officers responsible for ensuring product safety and meeting international standards, understanding GB/T 31485 is essential. R&D engineers can leverage insights from these tests to refine design iterations and improve future model performance. Procurement professionals may also benefit by using information derived from this standard to select suppliers who adhere to high quality and safety practices.
The test procedures outlined in GB/T 31485 involve several key steps:
- Setting up the vehicle on a crash test rig
- Positioning occupants according to specified guidelines
- Simulating various crash scenarios using controlled impacts
- Deploying airbags and recording data from sensors
- Evaluating deployment effectiveness based on predefined criteria
The results of these tests provide valuable feedback for continuous improvement efforts aimed at enhancing passive safety features in fuel cell vehicles. Compliance with GB/T 31485 not only helps manufacturers meet regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation and customer trust.
| Applied Standards |
|---|
| GB/T 31485:2019 - Safety Performance Requirements for Passive Safety Systems in Fuel Cell Vehicles |
The standard defines specific performance metrics, including deployment time, inflation rate, and coverage area of the airbag. These parameters are critical in determining whether a vehicle's passive safety system meets industry expectations.
Adhering to GB/T 31485 ensures that fuel cell vehicles have robust passive safety systems capable of protecting occupants effectively during accidents. This compliance contributes significantly to overall road safety and helps establish trust between manufacturers, regulators, and consumers.
Why It Matters
The importance of the GB/T 31485 standard cannot be overstated, especially considering the increasing popularity of fuel cell vehicles. As these vehicles gain market share, it becomes increasingly important to ensure they offer comparable levels of safety as traditional gasoline or diesel-powered cars.
Compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to producing safe and reliable vehicles, which is essential for gaining consumer confidence. Regulatory bodies rely on such standards when setting minimum requirements for passive safety systems in all types of automobiles. Adhering to these guidelines helps companies avoid costly recalls and potential legal issues associated with substandard products.
For R&D engineers involved in developing new models or improving existing ones, understanding the nuances of GB/T 31485 allows them to incorporate advanced technologies into their designs more effectively. By leveraging this knowledge, they can optimize deployment algorithms, enhance sensor accuracy, and refine material choices for better performance.
Quality managers play a crucial role in overseeing compliance with various standards like GB/T 31485. Their expertise ensures that production processes consistently meet or exceed specified criteria, thereby maintaining high standards of quality throughout the supply chain. This approach fosters long-term relationships with customers and stakeholders while promoting continuous improvement within organizations.
Compliance officers must stay abreast of changing regulations related to automotive safety. Keeping up-to-date with developments ensures they can implement necessary changes promptly without disrupting operations or affecting profitability negatively. Staying informed about evolving standards allows them to make strategic decisions that benefit both short-term goals and long-term sustainability plans for their organization.
Procurement professionals need to select suppliers who adhere strictly to high-quality practices, including those related to passive safety systems in fuel cell vehicles. By partnering with reputable vendors committed to meeting or exceeding specified criteria, they contribute towards achieving overall objectives set forth by regulatory authorities like GB/T 31485.
In summary, adherence to the GB/T 31485 standard is vital for maintaining industry leadership and fostering trust among consumers. It enables companies to meet stringent safety requirements while contributing positively to public health outcomes associated with road accidents involving fuel cell vehicles.
Applied Standards
| GB/T 31485:2019 - Safety Performance Requirements for Passive Safety Systems in Fuel Cell Vehicles |
|---|
| This standard specifies the safety performance requirements for passive safety systems, including airbag deployment characteristics and coverage areas. |
The GB/T 31485 standard provides detailed specifications on how to conduct tests that ensure fuel cell vehicles meet required safety standards. It covers aspects such as deployment times, inflation rates, and coverage areas for airbags used in these vehicles. Compliance with this standard demonstrates a commitment to producing safe and reliable vehicles.
The test procedures outlined in the standard involve setting up vehicles on crash test rigs, positioning occupants according to specified guidelines, simulating various crash scenarios using controlled impacts, deploying airbags, and recording data from sensors. Evaluation of deployment effectiveness is based on predefined criteria that ensure proper protection for occupants without causing harm through over-inflation or improper timing.
Adhering to GB/T 31485 ensures that fuel cell vehicles have robust passive safety systems capable of protecting occupants effectively during accidents. This compliance contributes significantly to overall road safety and helps establish trust between manufacturers, regulators, and consumers.
Customer Impact and Satisfaction
- Increased consumer confidence in the safety features offered by fuel cell vehicles
- Enhanced reputation for quality among manufacturers who comply with this standard
- Maintained regulatory compliance, avoiding costly recalls or legal issues
- Improved R&D capabilities through better understanding of testing procedures and criteria
- Better supplier selection based on adherence to high-quality practices related to passive safety systems
- Long-term relationships with customers and stakeholders built on trust and reliability
- Strategic decision-making influenced by staying informed about evolving standards, ensuring prompt implementation without disruption
The benefits of adhering to the GB/T 31485 standard extend beyond mere compliance; they contribute positively towards achieving overall objectives set forth by regulatory authorities. By ensuring that fuel cell vehicles meet or exceed specified criteria in terms of passive safety systems, manufacturers can enhance their reputation and build trust with consumers.
Increased consumer confidence stems directly from knowing that these vehicles undergo rigorous testing processes designed to protect occupants effectively during accidents. This level of assurance fosters greater acceptance and adoption rates for fuel cell vehicles across different markets worldwide.
The enhanced reputation enjoyed by manufacturers who comply with this standard translates into increased sales volumes due to improved brand perception among potential buyers. As more people trust the safety measures implemented within these vehicles, there is an inevitable increase in demand for such products.
Maintaining regulatory compliance helps companies avoid costly recalls or legal issues associated with substandard products. By adhering strictly to standards like GB/T 31485, firms can ensure that their offerings meet all necessary requirements set forth by relevant authorities worldwide.
Improved R&D capabilities arise from a deeper understanding of the testing procedures and criteria outlined in this standard. Engineers responsible for designing new models or refining existing ones gain valuable insights into optimizing deployment algorithms, enhancing sensor accuracy, and selecting materials that result in better overall performance.
Better supplier selection based on adherence to high-quality practices related to passive safety systems ensures consistency throughout the supply chain. When procurement professionals partner with reputable vendors committed to meeting or exceeding specified criteria, they contribute towards achieving long-term sustainability goals for their organizations.
Long-term relationships with customers and stakeholders are fostered by establishing trust through consistent compliance with relevant standards. This approach promotes continuous improvement within companies while benefiting all parties involved in the production process.
Strategic decision-making influenced by staying informed about evolving standards ensures prompt implementation without disruption to ongoing operations or profitability levels. By keeping abreast of changing regulations related to automotive safety, compliance officers can make well-informed choices that align with both short-term goals and long-term sustainability plans for their organizations.