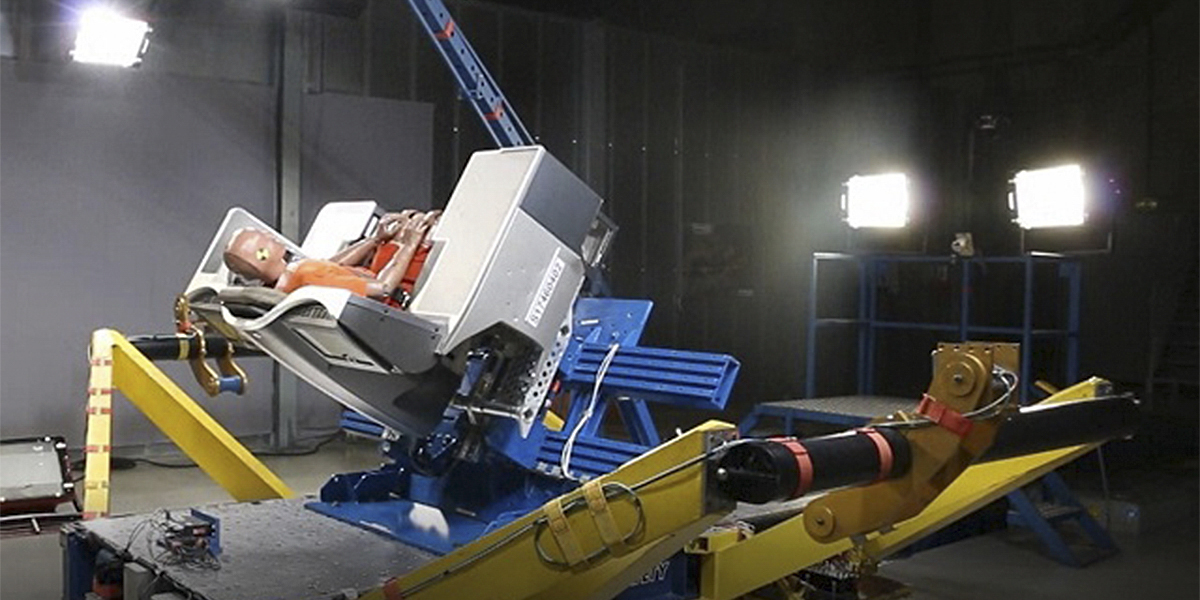
FMVSS 213 Child Restraint System Impact Testing
The Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 213, known as the "Child Restraint System" standard, is a critical regulation that ensures child safety in vehicles. This standard mandates rigorous testing to evaluate the performance of child restraint systems under simulated crash conditions. The primary goal is to ensure that these systems provide adequate protection for children during vehicle impacts.
FMVSS 213 specifies tests that simulate various types of crashes, including frontal impact and side impact scenarios. These tests are conducted using standardized test dummies representing different age groups, such as toddlers or preschool-aged children, to assess the effectiveness of restraint systems in real-world crash conditions.
The testing process is comprehensive and involves multiple stages. First, the child restraint system is installed in a vehicle according to manufacturer instructions. The vehicle is then subjected to controlled impact simulations using high-impact test equipment. Sensors within the dummy measure acceleration forces, deceleration rates, and other critical parameters during the simulated crash.
Following the test, detailed analysis of the dummy's response is conducted. This includes evaluating head movement, chest displacement, and overall restraint performance. The goal is to ensure that the system minimizes injury risk by effectively distributing impact forces away from vital areas like the head and chest.
The testing process also involves strict adherence to international standards such as ISO 16750-2 and SAE J213. These standards provide guidelines for testing methodologies, specimen preparation, and data interpretation. Compliance with these standards ensures that tests are conducted consistently across different laboratories and jurisdictions.
FMVSS 213 is particularly important in the context of automotive safety. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), child fatalities account for a significant portion of overall traffic-related deaths. Therefore, ensuring compliance with FMVSS 213 helps reduce these risks by mandating robust testing protocols.
For quality managers and R&D engineers involved in automotive safety, understanding and adhering to FMVSS 213 is crucial. Compliance officers must ensure that all child restraint systems meet the stringent requirements outlined in this standard. For procurement teams, selecting suppliers who adhere to these standards ensures that only high-quality products are used.
The testing process for FMVSS 213 involves several key steps:
- Installation of the child restraint system according to manufacturer specifications.
- Conducting controlled impact simulations using standardized crash test dummies.
- Evaluating dummy responses through detailed analysis, including head movement and chest displacement metrics.
The ultimate goal is to ensure that child restraint systems effectively protect children in the event of a vehicle collision. This comprehensive testing process helps manufacturers develop safer vehicles and products, ultimately contributing to improved road safety.
Scope and Methodology
| Test Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Frontal Impact Test | Involves simulating a collision where the vehicle's front is struck by another vehicle. This test evaluates how well the restraint system can prevent head and chest injury to occupants. |
| Side Impact Test | Replicates a situation where a vehicle collides with an object on its side, such as a pole or another vehicle. This test assesses the ability of the restraint system to protect against severe lateral impacts. |
| Dynamic Tests | Involves using dummies that move freely within the vehicle to simulate real-world crash scenarios. These tests provide insights into how well the restraint system performs under dynamic conditions. |
| Static Tests | Focus on evaluating the structural integrity of the child restraint system by subjecting it to static loads and forces, ensuring that it can withstand the rigors of a real crash. |
The methodology for FMVSS 213 testing is designed to simulate real-world crash conditions as closely as possible. This includes using standardized test dummies with specific anthropometric dimensions representing different age groups. The tests are conducted in controlled environments using high-precision impact equipment, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Compliance with FMVSS 213 is essential for manufacturers to ensure that their child restraint systems meet the highest safety standards. Failure to comply can result in fines, recalls, and damage to brand reputation. Therefore, it is crucial for automotive companies to invest in robust testing facilities and methodologies to meet these stringent requirements.
Benefits
- Increased Safety: FMVSS 213 ensures that child restraint systems are designed to minimize injury risk during vehicle collisions. This leads to better protection for children in the event of an accident.
- Compliance Assurance: Compliance with this standard helps manufacturers avoid legal penalties and recalls, thereby protecting their brand reputation.
- Innovation Drive: The rigorous testing requirements under FMVSS 213 encourage continuous improvement in child restraint system design. This fosters innovation and the development of safer products.
- Consumer Confidence: Meeting this standard instills confidence among consumers, as it ensures that their children are using safe and effective safety equipment.
The benefits extend beyond individual manufacturers to impact society at large by promoting better road safety. By ensuring that child restraint systems meet the highest standards, FMVSS 213 contributes to reducing traffic-related fatalities and injuries involving children.
Customer Impact and Satisfaction
- Enhanced Safety: Customers benefit from a significant reduction in risk for their children during vehicle collisions. This peace of mind is crucial for parents and guardians who value the safety of their loved ones.
- Increased Trust: Compliance with FMVSS 213 enhances customer trust, as it demonstrates a commitment to high standards of quality and safety.
- Positive Brand Image: Meeting these stringent requirements can enhance a manufacturer's brand image, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Competitive Advantage: Compliance with FMVSS 213 provides manufacturers with a competitive edge in the market, as it sets them apart from those who do not meet such high standards.
A satisfied customer base is essential for long-term success. By ensuring that child restraint systems comply with FMVSS 213, manufacturers can build and maintain strong relationships with their customers, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.