Repeatability and Reproducibility Testing for IVD Devices
Repeatability and reproducibility testing is a critical component of ensuring the accuracy, precision, and reliability of In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) devices. These tests are essential to validate that an IVD device consistently provides the same results under identical conditions, which is particularly important in medical diagnostics where even minor discrepancies can have significant clinical implications.
The repeatability test measures how closely multiple measurements agree with each other when performed by the same operator, using the same instrument and reagents on replicate samples. This ensures that the device’s performance remains consistent under the same conditions over time. Reproducibility tests assess the agreement between results obtained by different operators or laboratories using the same method but not necessarily the same equipment.
For an IVD device to be considered reliable, it must demonstrate both high repeatability and reproducibility within specified limits. This is often referred to as "within-laboratory" consistency and “between-laboratory” agreement. The variability in test results should fall well within the acceptable tolerances defined by regulatory standards.
The testing process involves several steps, including specimen preparation, calibration of instruments, and execution of tests according to predefined protocols. Specimens are typically prepared under strict quality control measures to ensure uniformity across all samples tested. Once prepared, they are analyzed multiple times using the same machine or different machines by various operators.
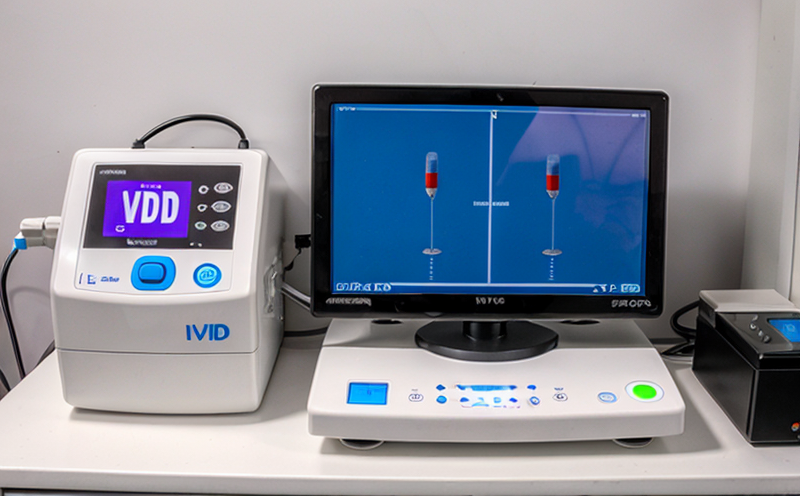
Instrumentation used in these tests includes automated analyzers capable of handling high throughput while maintaining precision and accuracy. The type of analyzer will depend on the specific IVD device being evaluated. For instance, chemiluminescent immunoassays may require different calibration procedures compared to enzyme-linked assays.
The results are then analyzed statistically using methods such as Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) or Coefficient of Variation (CV). These metrics help determine whether the observed variations fall within acceptable thresholds set forth by relevant standards and guidelines. Regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and WHO have established criteria for what constitutes adequate repeatability and reproducibility.
Failure to meet these requirements could lead to incorrect diagnoses or treatment decisions based on faulty test results. Therefore, rigorous testing ensures that only accurate and reliable IVD devices reach clinical use.
In summary, conducting thorough repeatability and reproducibility tests is crucial for maintaining the integrity of diagnostic outcomes across various settings. By adhering strictly to established protocols and leveraging advanced analytical tools, laboratories can ensure consistent performance metrics that support effective patient care decisions.
| Applied Standards |
|---|
| ISO 17025:2017 – General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories |
| CLIA '88 (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments) |
| European Commission Guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Regulations |
| ISO 15195-2:2016 – Medical Devices - In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) - Part 2: Quality Requirements for the Production, Installation and Servicing of IVD Medical Devices |
The above standards provide comprehensive guidelines on how to conduct repeatability and reproducibility tests effectively. Compliance with these regulations not only enhances trustworthiness but also ensures that your laboratory meets international quality assurance benchmarks.
Applied Standards
- ISO 17025:2017 – General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories
- CLIA '88 (Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments)
- European Commission Guidelines on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Regulations
- ISO 15195-2:2016 – Medical Devices - In Vitro Diagnostic (IVD) - Part 2: Quality Requirements for the Production, Installation and Servicing of IVD Medical Devices
These standards provide a framework for conducting rigorous repeatability and reproducibility testing ensuring that laboratories meet stringent quality assurance requirements.
International Acceptance and Recognition
- The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepts results from internationally recognized proficiency tests.
- The European Medicines Agency (EMA) requires compliance with ISO 17025 standards for laboratory operations.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends adherence to CLIA '88 for clinical laboratories worldwide.
By participating in these programs and adhering to such stringent international standards, your laboratory can ensure that its testing capabilities are widely accepted across borders.
Environmental and Sustainability Contributions
In addition to ensuring high-quality diagnostic outcomes, laboratories play a vital role in promoting environmental sustainability. Implementing efficient resource management practices can significantly reduce waste generation and operational costs associated with IVD testing.
One way to achieve this is by optimizing specimen collection processes to minimize sample loss during transport or storage. This reduces the amount of reagents needed for subsequent analyses, thereby cutting down on chemical disposal requirements.
Laboratories can also adopt energy-efficient practices such as using LED lighting systems and motion sensor controls in areas where lights are not always required. Additionally, recycling waste materials like plastic containers and glassware helps reduce landfill contributions while fostering a culture of responsibility towards the environment.
By embracing these sustainable measures, laboratories contribute positively to both public health initiatives and global environmental goals. This aligns with broader objectives outlined by international bodies concerned about climate change mitigation efforts.