ASTM F2568 Testing of Modular Orthopedic Connections
The ASTM F2568 standard provides a method to evaluate the fatigue behavior and cyclic loading performance of modular orthopedic connections used in hip and knee implants. This testing is critical for ensuring that these components can withstand the stresses associated with everyday movement, thereby enhancing patient safety and the longevity of surgical outcomes.
The ASTM F2568 test simulates real-world conditions by subjecting the connection to cyclic loading until failure occurs. This helps manufacturers identify potential design flaws early in the development process, ensuring that products meet stringent performance requirements before they reach clinical use.
Before delving into specific details of the testing procedure, it is important to understand the context within which ASTM F2568 operates. Orthopedic and prosthetic devices are designed to restore function to patients who have suffered injuries or loss due to various reasons such as trauma, disease, or congenital abnormalities. The modular nature of these implants allows for customization based on individual patient needs, but it also introduces complexity in terms of ensuring compatibility and performance across different components.
The ASTM F2568 test focuses specifically on the connection between the femoral component and the acetabular cup within hip replacement systems. This connection is subject to significant stress during walking, climbing stairs, or any other activity involving weight-bearing motion. By assessing how well this connection holds up under repeated loading cycles, manufacturers can optimize their designs for durability and reliability.
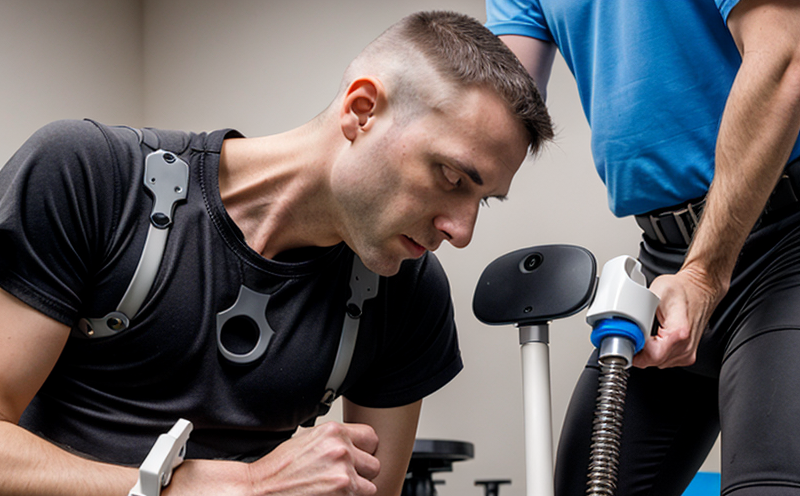
To perform ASTM F2568 testing, specialized equipment such as fatigue testers equipped with specific fixtures is required. These machines simulate the forces experienced by the implant during use, allowing engineers to observe both the structural integrity of the connection and any signs of wear or damage over time.
| Test Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Cyclic Loading | The application of varying levels of force repeatedly to simulate normal usage conditions. |
| Load Range | The range within which the test is conducted, typically between 0.5 and 1.5 times the expected maximum load in actual use. |
| Frequency | The number of cycles per minute at which loading occurs, usually set according to industry standards. |
| Monitoring | Continuous observation of the connection for any signs of failure or degradation during testing. |
The specimen preparation process involves carefully selecting and preparing samples that accurately represent the intended use of the implant. This includes cleaning, sterilizing, and positioning the components in a manner that reflects real-world usage scenarios as closely as possible. Proper sample preparation is crucial for obtaining reliable test results.
Once prepared, the specimens are loaded into the fatigue tester according to ASTM F2568 specifications. The machine then applies cyclic loading at specified parameters until failure occurs or predetermined cycle counts have been reached. Throughout this process, data on stress levels, strain rates, and other relevant factors are collected for analysis.
After completion of testing, comprehensive reports detailing the results are generated. These reports include information about the number of cycles before failure, any observed failures modes (such as cracking or deformation), and comparisons against baseline data from similar tests conducted on previous versions of the product.
ASTM F2568 is widely recognized by regulatory bodies around the world for its role in ensuring high standards of quality and safety in orthopedic implants. Compliance with this standard helps manufacturers meet stringent requirements set forth by organizations like the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and other national authorities responsible for overseeing medical device approvals.
Understanding ASTM F2568 testing is essential not only for those involved directly in R&D but also for quality managers, compliance officers, and procurement teams working with orthopedic companies. By staying informed about current practices and trends in this area, stakeholders can make more informed decisions regarding product development, manufacturing processes, and regulatory compliance.
Scope and Methodology
- Identifies the specific components of modular hip implants subjected to testing.
- Details the range of loading conditions used in simulating real-world usage scenarios.
- Describes the criteria for determining when a specimen has failed during testing.
| Test Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Range | The specified range within which cyclic loading occurs, ensuring accurate simulation of actual usage conditions. |
| Cyclic Loading Frequency | The rate at which loads are applied during each cycle, influencing the overall stress experienced by the connection under test. |
| Monitoring Techniques | Methods employed to continuously observe the specimen for any signs of failure or degradation throughout testing. |
The ASTM F2568 standard provides clear guidelines on how to conduct these tests, including details on specimen preparation, equipment setup, and data collection procedures. Compliance with these standards ensures that results are consistent across different laboratories conducting similar tests, promoting greater confidence in the accuracy of reported findings.
By following rigorous testing protocols outlined in ASTM F2568, manufacturers can ensure their products meet stringent regulatory requirements while also providing safer, more effective solutions for patients undergoing orthopedic surgeries. This commitment to quality and innovation is reflected not only in the final product but also in ongoing efforts to improve test methods and expand our understanding of how best to evaluate these complex medical devices.
International Acceptance and Recognition
- The ASTM F2568 standard has been adopted by regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA (Food and Drug Administration).
- It is recognized as an essential tool for ensuring compliance with international standards of quality and safety in medical device manufacturing.
ASTM F2568 testing plays a crucial role in meeting global regulatory requirements for orthopedic implants. Many countries have adopted this standard due to its comprehensive approach to evaluating the fatigue behavior and cyclic loading performance of modular connections used in hip and knee replacements. The FDA, among others, requires manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with ASTM standards as part of their approval processes.
Recognition of ASTM F2568 extends beyond mere acceptance by regulatory agencies; it also reflects broader industry consensus on best practices for testing such devices. Many leading orthopedic companies incorporate this standard into their quality assurance programs, ensuring that every new product undergoes thorough evaluation before being introduced to market.
In addition to its widespread adoption, ASTM F2568 continues to evolve as researchers gain deeper insights into the challenges posed by modular connections in modern orthopedics. Regular updates to the standard reflect these advancements, maintaining relevance and utility for practitioners across various regions and countries.
Use Cases and Application Examples
- Evaluating the fatigue resistance of new hip implant designs.
- Comparing different materials used in modular connections to identify superior options.
| Test Results | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue Life | The number of cycles before failure, providing insight into the longevity of a given design. |
| Failure Modes | Type and location of any observed failures, helping guide improvements in future iterations. |
| Material Performance | Comparison between various materials used to construct modular connections, highlighting strengths and weaknesses. |
ASTM F2568 testing offers valuable insights into the performance of modular orthopedic connections through a variety of use cases. For instance, manufacturers can employ this method when developing new hip implant designs to ensure they meet necessary durability standards before introduction to market.
In another scenario, comparing different materials used in these connections allows researchers to identify which options offer superior fatigue resistance or better overall performance under cyclic loading conditions. This comparative analysis helps inform material selection decisions throughout the product lifecycle.
Furthermore, ASTM F2568 testing provides a platform for evaluating existing products against established criteria, allowing manufacturers to make informed improvements based on empirical data rather than relying solely on theoretical considerations. Such continuous improvement efforts contribute significantly towards enhancing patient outcomes and reducing instances of revision surgeries due to implant failure or wear.
Real-world application examples further underscore the importance of ASTM F2568 testing in ensuring reliable performance across diverse clinical settings. By incorporating this standard into their quality assurance programs, orthopedic companies not only meet regulatory expectations but also contribute towards advancing the field of medical technology through rigorous evaluation practices.