JIS S 1103 Mechanical Strength Testing of Children’s Beds and Chairs
The JIS S 1103 standard is a critical requirement for ensuring the mechanical strength of children's furniture in Japan. This test evaluates the resistance to collapse or deformation under specified loading conditions, which is essential for safeguarding child safety.
Children's beds and chairs are designed with specific ergonomic considerations to ensure comfort while also providing adequate support. The mechanical strength testing ensures that these products not only meet aesthetic expectations but also function safely in real-world scenarios. This test applies particularly stringent requirements due to the potential risks involved, especially for young children who may be less capable of assessing or avoiding hazards.
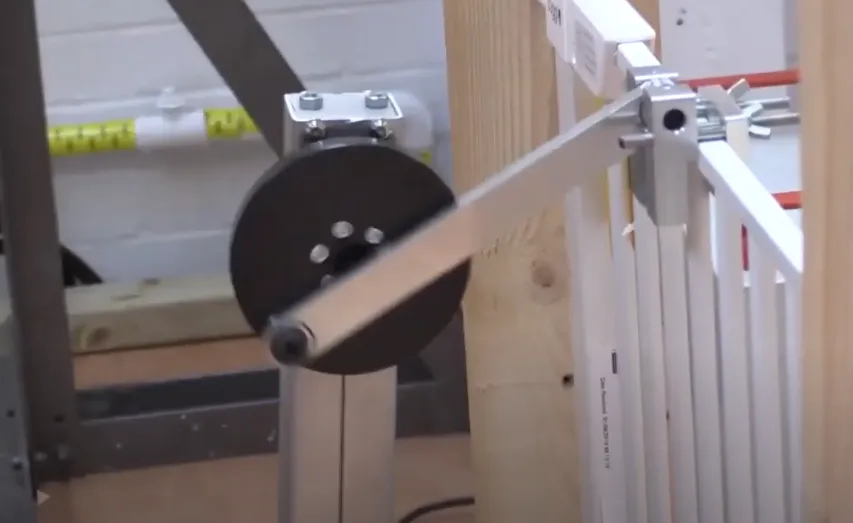
During this test, a load is applied to the furniture piece according to JIS S 1103 specifications to determine if it will withstand typical usage and abuse. The testing apparatus typically includes a loading frame that can apply forces in multiple directions as per the standard's requirements. Specimens are carefully prepared by ensuring they represent a typical product design for market sale.
The acceptance criteria for this test are stringent, aiming to prevent any collapse or deformation under anticipated usage conditions. The JIS S 1103 standard defines specific load values and holding times that the furniture must endure without failing. This ensures that the furniture can support a child's weight and movements safely.
The significance of this test cannot be overstated, especially in light of recent incidents where poorly designed or manufactured children's furniture led to accidents. By adhering to JIS S 1103 standards, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety, thereby protecting the well-being of children.
Quality managers and compliance officers must ensure that all products comply with these stringent requirements. R&D engineers play a crucial role in designing furniture that meets or exceeds these standards while also being functional and aesthetically pleasing. Procurement teams must verify that suppliers are capable of delivering components that will contribute to a product meeting JIS S 1103.
The mechanical strength testing process involves careful preparation, application of standardized loads, and thorough inspection for any signs of failure. This ensures that the results are reliable and reproducible, providing confidence in the safety and durability of the furniture.
By adhering to JIS S 1103 standards, manufacturers can ensure their products meet or exceed regulatory requirements, thereby safeguarding children's health and well-being. The testing process is not only about compliance but also about fostering a culture of quality and safety in product development.
Quality and Reliability Assurance
Ensuring the mechanical strength of children’s furniture is paramount to maintaining high standards of reliability and quality. The JIS S 1103 standard provides a robust framework for testing that helps manufacturers achieve these goals.
The process begins with careful specimen preparation, where each piece of furniture undergoes rigorous inspection to ensure it meets the specified design criteria. This includes checking dimensions, materials, and assembly quality before loading tests can commence.
The testing apparatus used for JIS S 1103 is highly specialized and designed to apply precise loads in multiple directions, simulating real-world conditions children might encounter when using furniture. The reliability of this equipment is crucial, as any discrepancies could lead to inaccurate results. Regular calibration and maintenance are essential to ensure consistent and accurate testing.
Data collection during the test is meticulous, with detailed records kept for each specimen tested. This data includes not only the load applied but also observations on how the furniture responds under stress. Any deviations from expected behavior can be immediately identified, allowing for quick adjustments in production processes to prevent future failures.
The reliability of these tests is further enhanced by adherence to international standards such as JIS S 1103. These standards provide a clear and universally accepted set of criteria that manufacturers can follow, ensuring consistency across different regions and markets. This global recognition adds another layer of confidence in the quality and safety of products.
In summary, the mechanical strength testing process under JIS S 1103 is designed to ensure high levels of reliability and quality. By following these stringent protocols, manufacturers can produce furniture that not only meets but exceeds regulatory requirements, thereby safeguarding children’s health and well-being.
Customer Impact and Satisfaction
The mechanical strength testing of children's beds and chairs under JIS S 1103 has a profound impact on customer satisfaction. Parents and guardians are increasingly aware of the importance of safety when it comes to their children’s furniture, and compliance with this standard is seen as a mark of quality and reliability.
By ensuring that products meet or exceed these stringent requirements, manufacturers can build trust with customers. This trust translates into higher customer satisfaction, repeat purchases, and positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend the brand to others, which in turn expands market reach and customer loyalty.
Moreover, compliance with JIS S 1103 can help businesses avoid costly recalls and legal disputes. Non-compliance could lead to product liability claims or safety warnings from authorities, all of which can damage a company’s reputation and financial health. By adhering to these standards, companies demonstrate their commitment to quality and safety, thereby reducing risks and enhancing brand reputation.
The testing process also provides valuable feedback for continuous improvement. Manufacturers can use the insights gained from testing to refine product designs and manufacturing processes, leading to even higher-quality products in the future. This iterative approach ensures that products are not only safe but also optimized for performance and durability.
In conclusion, mechanical strength testing under JIS S 1103 is crucial not just for regulatory compliance but also for enhancing customer satisfaction and building long-term relationships with consumers. By prioritizing safety and quality, manufacturers can create a positive impact on both their business and the well-being of their customers.
International Acceptance and Recognition
The JIS S 1103 standard is widely recognized and accepted internationally for its rigorous approach to mechanical strength testing in children's furniture. Its acceptance extends beyond Japan, influencing global standards for safety and quality.
Many countries look to JIS S 1103 as a benchmark due to its comprehensive nature and stringent criteria. This standard has influenced the development of other international standards such as ASTM F2957 in the United States, which also focuses on mechanical performance but adapts some aspects for local market conditions.
Manufacturers who comply with JIS S 1103 can export their products to various markets with greater ease. Compliance provides a strong competitive advantage by demonstrating adherence to high-quality standards that are respected worldwide. This recognition enhances the brand’s reputation and opens doors to international buyers and distributors.
The standard's global acceptance also reflects its importance in promoting safety across different cultures and regions. By adhering to JIS S 1103, manufacturers ensure their products meet or exceed the expectations of consumers worldwide, fostering a safer environment for children wherever they are used.
In summary, the international recognition of JIS S 1103 underscores its significance in promoting safety and quality standards. This acceptance not only facilitates global trade but also reinforces the commitment to child safety that is integral to this testing process.