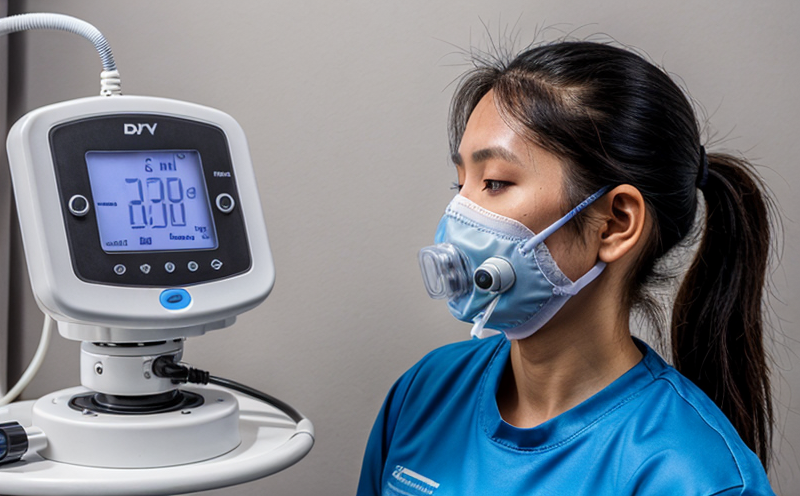
ISO 23328 Breathing System Filters Bacterial Filtration Efficiency Testing
The ISO 23328 standard is a critical protocol used to evaluate the bacterial filtration efficiency (BFE) of breathing system filters, which are essential components in respiratory and ventilation devices. These filters play a pivotal role in safeguarding against microbial contamination, ensuring that air supplied to patients or users meets stringent hygiene standards. The testing process outlined by ISO 23328 is designed to mimic real-world operating conditions and provides a standardized method for assessing the performance of these critical components.
BFE testing involves exposing the filter to an aerosolized bacterial suspension, typically Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538), and measuring the percentage of bacteria that pass through the filter. This test is crucial for medical devices used in hospitals, operating theaters, intensive care units, and other healthcare settings where infection control is paramount. The results provide assurance that the filters can effectively protect against microbial contamination, thereby enhancing patient safety.
The testing procedure requires precise control over environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and airflow to ensure accurate and reproducible results. Compliance with ISO 23328 ensures that manufacturers adhere to international standards for quality and reliability, which is essential in the medical device industry where product performance can directly impact patient health.
The testing facility must be equipped with a specialized aerosol generator capable of producing an aerosolized bacterial suspension at a specific concentration. The filter being tested is placed between the aerosol source and a collection chamber. After exposure, the collected bacteria are quantified using a viable plate count method. This process allows for the calculation of BFE, which is expressed as a percentage.
The importance of ISO 23328 testing extends beyond mere compliance; it reflects an ongoing commitment to patient safety and healthcare quality. By adhering to this standard, manufacturers can demonstrate that their products meet or exceed industry expectations in terms of hygiene and effectiveness. This, in turn, fosters trust among healthcare providers and patients alike.
The scope of ISO 23328 testing is not limited to respiratory devices alone but also encompasses ventilation systems used in various medical settings. The standard ensures that the filters employed in these systems are capable of maintaining a sterile environment, which is particularly critical in environments where the risk of infection transmission is high.
Quality managers and compliance officers can leverage ISO 23328 testing to ensure that their products meet regulatory requirements. R&D engineers benefit from this standardized protocol as it provides clear guidelines for filter design and optimization. Procurement teams can use these results to select suppliers who adhere to the highest quality standards.
Scope and Methodology
| Test Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Aerosol Generator | Produces an aerosolized bacterial suspension (ATCC 6538) at a specified concentration. |
| Filter Setup | The filter is placed between the aerosol source and collection chamber to simulate real-world conditions. |
| Airflow Control | Ensures consistent airflow during testing for accurate measurement of bacterial filtration efficiency. |
| Bacterial Collection | Collected bacteria are quantified using a viable plate count method to determine BFE percentage. |
| Temperature and Humidity Control | Maintains stable environmental conditions to ensure reproducibility of results. |
| Data Analysis | Calculates the BFE percentage based on the number of bacteria that pass through the filter versus those collected. |
The testing process begins with the preparation of a bacterial suspension, typically using Staphylococcus aureus. The aerosol generator then produces an aerosolized form of this suspension, which is directed towards the filter under controlled conditions. After exposure, the collected bacteria are quantified to determine the percentage that has passed through the filter. This value represents the BFE efficiency.
The use of a viable plate count method ensures accurate and reliable results. This methodology involves collecting samples from both sides of the filter and culturing them on appropriate media. The number of colonies formed is then counted, allowing for the calculation of BFE percentage. This process must be conducted under stringent quality control measures to ensure consistent and reproducible results.
The testing facility must maintain strict adherence to ISO 23328 standards throughout the entire procedure. This includes ensuring that all equipment is calibrated correctly before use and that environmental conditions are precisely controlled. The facility should also have robust quality assurance protocols in place to minimize variability and ensure accurate results.
The standard specifies detailed procedures for each step of the testing process, from aerosol generation to data analysis. Compliance with these guidelines ensures that the results obtained are reliable and can be trusted by regulatory bodies and end-users alike. The facility must also have a comprehensive record-keeping system in place to document all aspects of the test, including equipment calibration, environmental conditions, and operator actions.
The importance of accurate testing cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts patient safety and healthcare quality. By adhering to ISO 23328 standards, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to producing high-quality products that meet or exceed industry expectations. This, in turn, fosters trust among healthcare providers and patients who rely on these devices for critical care.
Quality and Reliability Assurance
The quality assurance process plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of ISO 23328 BFE testing. Rigorous calibration of all testing equipment is essential to maintain consistent results. This includes regular checks on the aerosol generator, collection chambers, and other components involved in the test setup.
Environmental control is another critical aspect of quality assurance. Temperature, humidity, and airflow must be precisely regulated throughout the testing process to ensure that all conditions are identical for each sample. Variability in these factors could lead to inaccurate BFE readings, thereby compromising the integrity of the results.
Data analysis also requires meticulous attention to detail. The number of bacterial colonies counted from both sides of the filter provides a direct measure of BFE efficiency. Any discrepancies or errors in this step can significantly affect the final outcome. Therefore, operators must undergo thorough training and follow standardized procedures to minimize human error.
The testing facility should have robust quality assurance protocols in place, including regular audits and inspections by independent third parties. These measures help identify and rectify any potential issues before they impact the results. Additionally, continuous improvement initiatives ensure that the facility remains up-to-date with the latest standards and practices.
Compliance with ISO 23328 not only ensures high-quality testing but also enhances patient safety and healthcare quality. By adhering to this international standard, manufacturers can demonstrate their commitment to producing reliable products. This fosters trust among healthcare providers and patients who rely on these devices for critical care.
The importance of accurate testing cannot be overstated. It directly impacts the performance and effectiveness of respiratory and ventilation system filters. By ensuring that all aspects of the test are conducted correctly, facilities can provide manufacturers with reliable data that meets or exceeds regulatory requirements.
International Acceptance and Recognition
The ISO 23328 standard is widely recognized and accepted across various international jurisdictions. Its adoption by regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders underscores its importance in ensuring the safety and efficacy of breathing system filters used in medical devices.
Countries around the world have incorporated ISO 23328 into their national regulations, further emphasizing its significance in global healthcare standards. Regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Commission (EC), and other similar bodies use this standard to assess compliance with international quality requirements.
The widespread acceptance of ISO 23328 by these regulatory entities ensures that manufacturers can confidently market their products globally without facing compatibility issues in different regions. This harmonization of standards simplifies the process for companies operating across multiple markets, reducing administrative burdens and enhancing efficiency.
Industry associations and professional bodies also recognize the value of ISO 23328. They endorse its use as a benchmark for evaluating the performance of breathing system filters in various applications. By aligning with this international standard, manufacturers can position themselves favorably within competitive markets by demonstrating adherence to best practices.
The harmonization of standards through widespread recognition contributes to improved patient safety and healthcare quality worldwide. Regulatory bodies benefit from consistent testing methods that yield reliable data, facilitating more effective oversight and decision-making processes. Healthcare providers gain confidence in the products they use, knowing that these devices have been rigorously tested against internationally recognized criteria.
The global acceptance of ISO 23328 reflects its role as a cornerstone in ensuring the safety and efficacy of breathing system filters used in medical devices. By adhering to this standard, manufacturers can ensure consistent performance across diverse environments while meeting regulatory expectations globally.