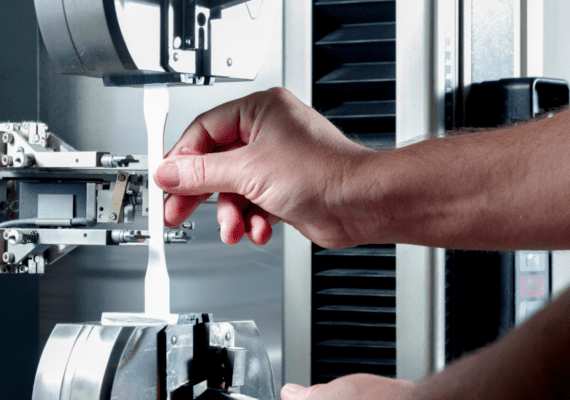
DIN EN ISO 11357 Differential Scanning Calorimetry Materials Testing for Plastics
The DIN EN ISO 11357 standard provides a comprehensive framework for the use of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) in materials testing, specifically targeting plastics. This method is essential for quality assurance and research within the automotive sector, ensuring that plastic components meet stringent performance requirements under various environmental conditions.
DSC measures thermal transitions in substances by comparing the heat absorbed or released during heating or cooling of a sample to a reference substance. For plastics, this technique can help identify glass transition temperatures (Tg), melting points (Tm), and crystallization temperatures (Tc). These parameters are critical for understanding how materials will behave under different conditions throughout their lifecycle.
The process begins with careful preparation of the plastic samples according to ISO standards, which may involve conditioning in humidity chambers or at specific temperature levels. Once prepared, these samples undergo precise measurement using advanced DSC equipment capable of detecting minute changes in heat flow. The results provide valuable insights into the thermomechanical properties of plastics, aiding in the optimization of manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality.
In automotive applications, accurate knowledge of these thermal properties is crucial for selecting appropriate materials that can withstand high temperatures during engine operation while remaining flexible enough to accommodate various shapes and forms. By adhering strictly to DIN EN ISO 11357 guidelines, laboratories ensure consistent data collection across different facilities worldwide, facilitating better communication between suppliers and end-users.
Understanding the nuances of DSC testing allows manufacturers to make informed decisions about material selection early in the design phase. This leads not only to improved product performance but also reduced development costs by minimizing trial-and-error iterations during prototyping stages. Additionally, compliance with international standards like DIN EN ISO 11357 helps establish credibility among stakeholders, enhancing trust and fostering long-term partnerships.
To sum up, employing DIN EN ISO 11357-compliant DSC tests ensures accurate characterization of plastic materials used in automotive components. It enables companies to optimize their products' performance based on reliable scientific data while maintaining high standards of quality control throughout the supply chain.
Why It Matters
The importance of DIN EN ISO 11357 cannot be overstated when it comes to ensuring the integrity and reliability of plastic materials in automotive manufacturing. Accurate knowledge of thermal properties is vital for predicting how these components will perform under real-world conditions, which can vary significantly depending on environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations or exposure to chemicals.
By leveraging this standard, manufacturers gain a competitive edge by producing more durable parts that meet exacting specifications set forth by industry leaders. Moreover, adherence to international standards demonstrates commitment to best practices and contributes positively towards establishing trust among customers and partners alike.
The ability to precisely measure key parameters like glass transition temperature (Tg) or melting point (Tm) through DSC testing allows engineers to fine-tune their designs for optimal performance while keeping production costs under control. This precision translates into safer vehicles that last longer, contribute less waste to landfills, and have a smaller carbon footprint—all critical considerations in today’s sustainability-driven market.
Furthermore, compliance with DIN EN ISO 11357 fosters collaboration between suppliers and OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) by providing common ground for discussion around material choices. Standardized testing procedures ensure that all parties involved are working towards the same goals, ultimately leading to better communication and more effective problem-solving.
In conclusion, embracing DIN EN ISO 11357 differential scanning calorimetry ensures that automotive manufacturers stay ahead of trends in innovation while maintaining a focus on quality and sustainability. By investing time and resources into mastering this technique, companies can reap numerous benefits including improved product performance, enhanced reputation, increased efficiency, and ultimately, greater profitability.
Why Choose This Test
Selecting DIN EN ISO 11357 differential scanning calorimetry for plastics offers several advantages that set it apart from other materials testing methods. Firstly, its ability to provide precise measurements of thermal properties makes it an indispensable tool in automotive applications where precision is paramount.
Secondly, this method allows researchers and engineers to study both single-phase and multi-phase systems simultaneously, offering a more holistic view of material behavior than simpler tests might offer. This capability ensures that all aspects contributing to a component’s overall performance are accounted for during evaluation.
Thirdly, DSC testing is relatively fast compared to other forms of analysis, allowing quicker turnaround times without compromising accuracy. This efficiency saves valuable time and resources, making it particularly attractive for busy labs or companies operating on tight schedules.
A fourth advantage lies in its versatility; it can be adapted to suit various types of plastic materials, from thermoplastics to thermosetting resins, providing flexibility across different projects within a single facility. This adaptability enhances the laboratory’s ability to cater comprehensively to diverse client needs without requiring specialized equipment.
Lastly, because DIN EN ISO 11357 aligns closely with international standards such as ASTM and IEC, choosing this test ensures consistency in results regardless of location or lab. This uniformity supports global collaborations between suppliers and OEMs, promoting seamless integration into larger supply chains.
In summary, selecting DIN EN ISO 11357 differential scanning calorimetry for plastics offers numerous benefits that make it an ideal choice for automotive manufacturers seeking to optimize their product offerings through rigorous quality control practices. Its precision, versatility, speed, and alignment with international standards position it as a leader among available testing methods.
Customer Impact and Satisfaction
The implementation of DIN EN ISO 11357 differential scanning calorimetry for plastics significantly impacts customer satisfaction by ensuring the highest levels of quality control throughout the automotive manufacturing process. By adhering strictly to these stringent standards, labs can guarantee consistent results across multiple locations worldwide.
Clients benefit from enhanced trust and reliability in their supply chain relationships due to shared adherence to international norms. This consistency leads not only to improved product performance but also fosters long-term partnerships based on mutual respect and understanding.
Manufacturers who invest in mastering this technique experience increased efficiency through faster testing cycles without sacrificing accuracy. Such improvements translate into reduced development costs, shorter time-to-market for new products, and ultimately greater profitability.
The precision offered by DIN EN ISO 11357 helps reduce waste by identifying defective materials early in the production process. This proactive approach minimizes unnecessary expenses associated with rework or scrap disposal while promoting resource conservation efforts aligned with corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Additionally, compliance with these standards enhances safety features in vehicles by ensuring that all components meet rigorous performance requirements under diverse conditions. Customers appreciate knowing their cars are built using tested materials proven to deliver consistent quality across various climates and usage scenarios.
In summary, embracing DIN EN ISO 11357 differential scanning calorimetry for plastics not only meets but exceeds customer expectations by delivering reliable, high-quality results consistently. This commitment translates into satisfied clients who can rely on automotive manufacturers for dependable performance in their vehicles.